




業(yè)務(wù)咨詢
中國(guó):
Email: marketing@medicilon.com.cn
業(yè)務(wù)咨詢專線:400-780-8018
(僅限服務(wù)咨詢,其他事宜請(qǐng)撥打川沙總部電話)
川沙總部電話: +86 (21) 5859-1500
海外:
+1(781)535-1428(U.S.)
0044 7790 816 954 (Europe)
Email:marketing@medicilon.com
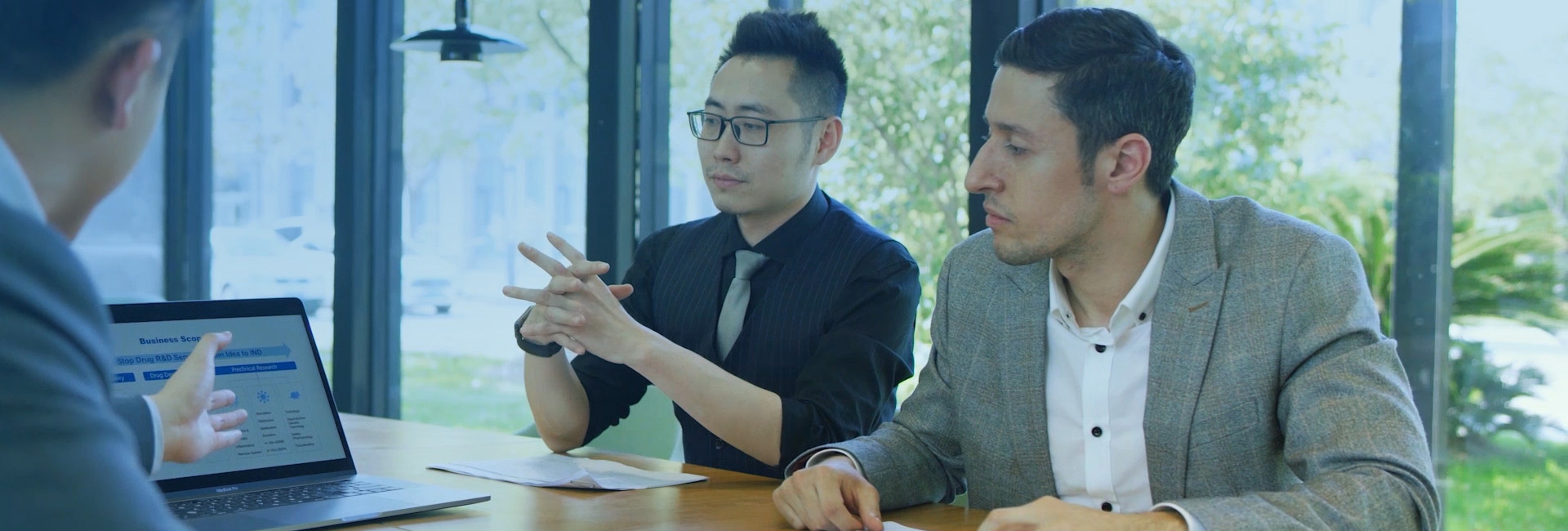




Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is the most common animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), a neuroinflammatory and demyelinating disease characterized by multifocal perivascular infiltrates of immune cells. Although EAE is predominantly considered a T helper 1-driven autoimmune disease, mounting evidence suggests that activated dendritic cells (DC), which are the bridge between innate and adaptive immunity, also contribute to its pathogenesis. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6), a NAD+-dependent deacetylase involved in genome maintenance and in metabolic homeostasis, regulates DC activation, and its pharmacological inhibition could, therefore, play a role in EAE development.
The PK study was performed by Medicilon.
 Reference:
Reference:
 相關(guān)新聞
相關(guān)新聞